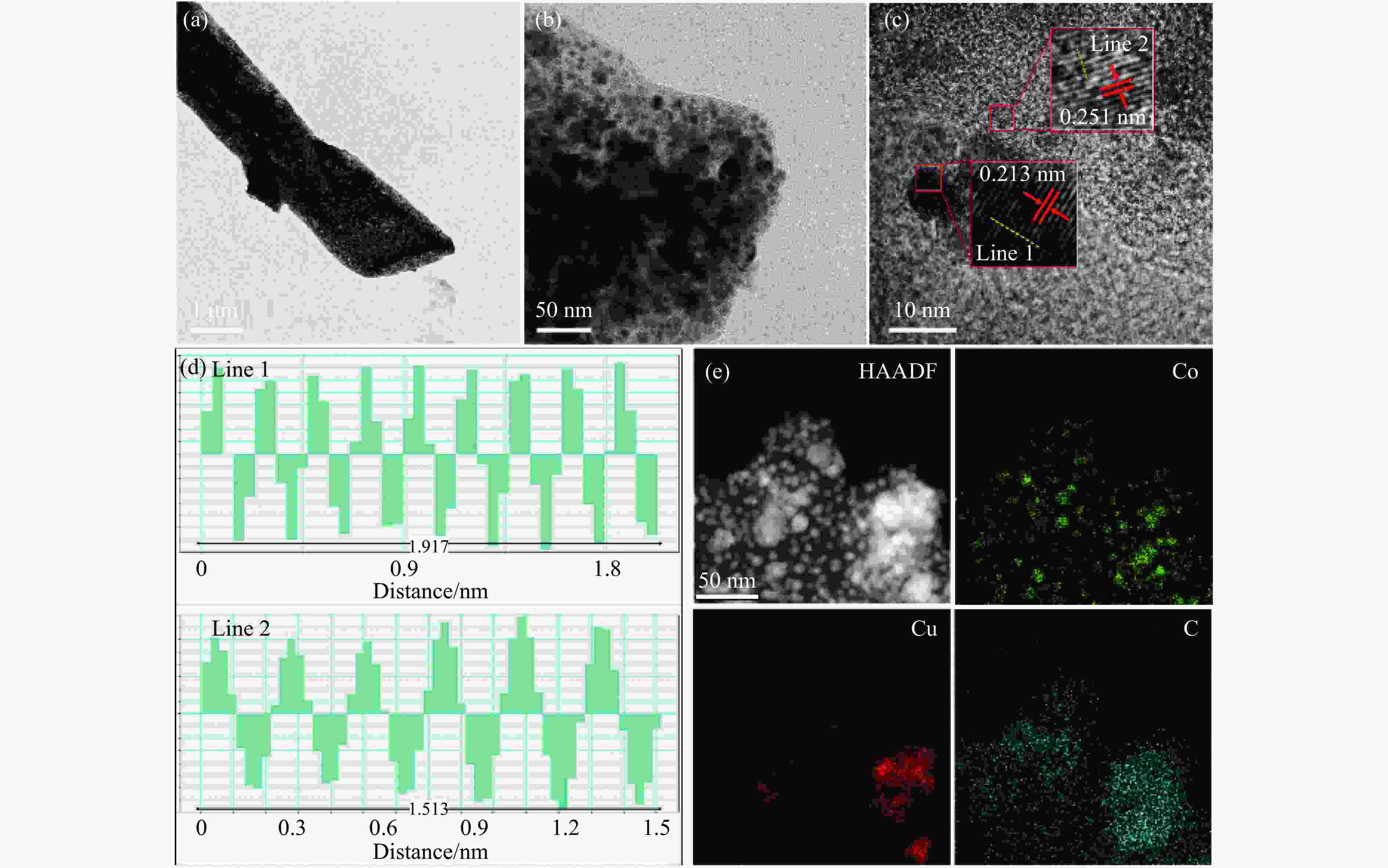
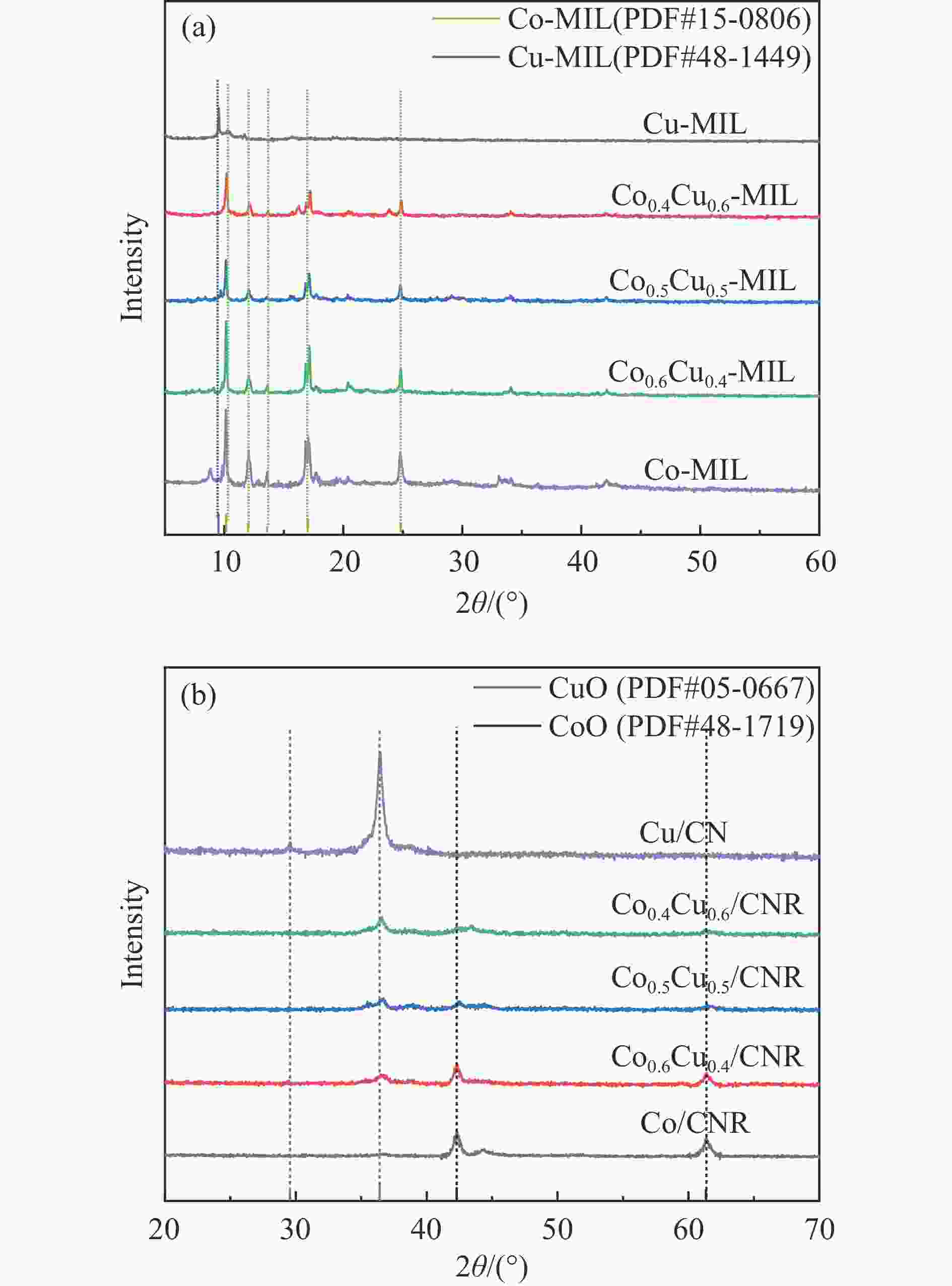
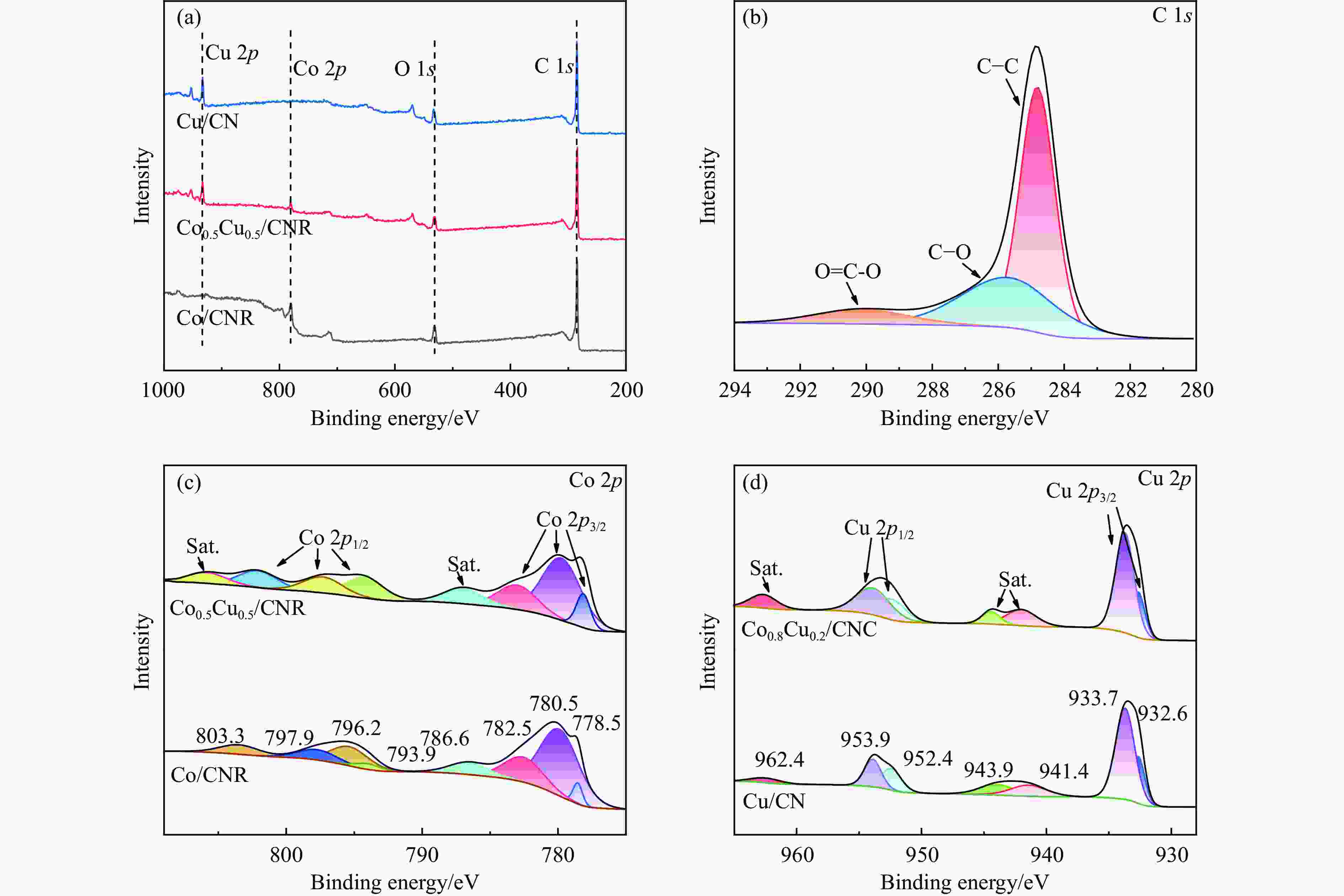
Preparation of Co0.5Cu0.5/CNR catalyst and its performance in hydrogen production by hydrolysis of ammonia borane
-
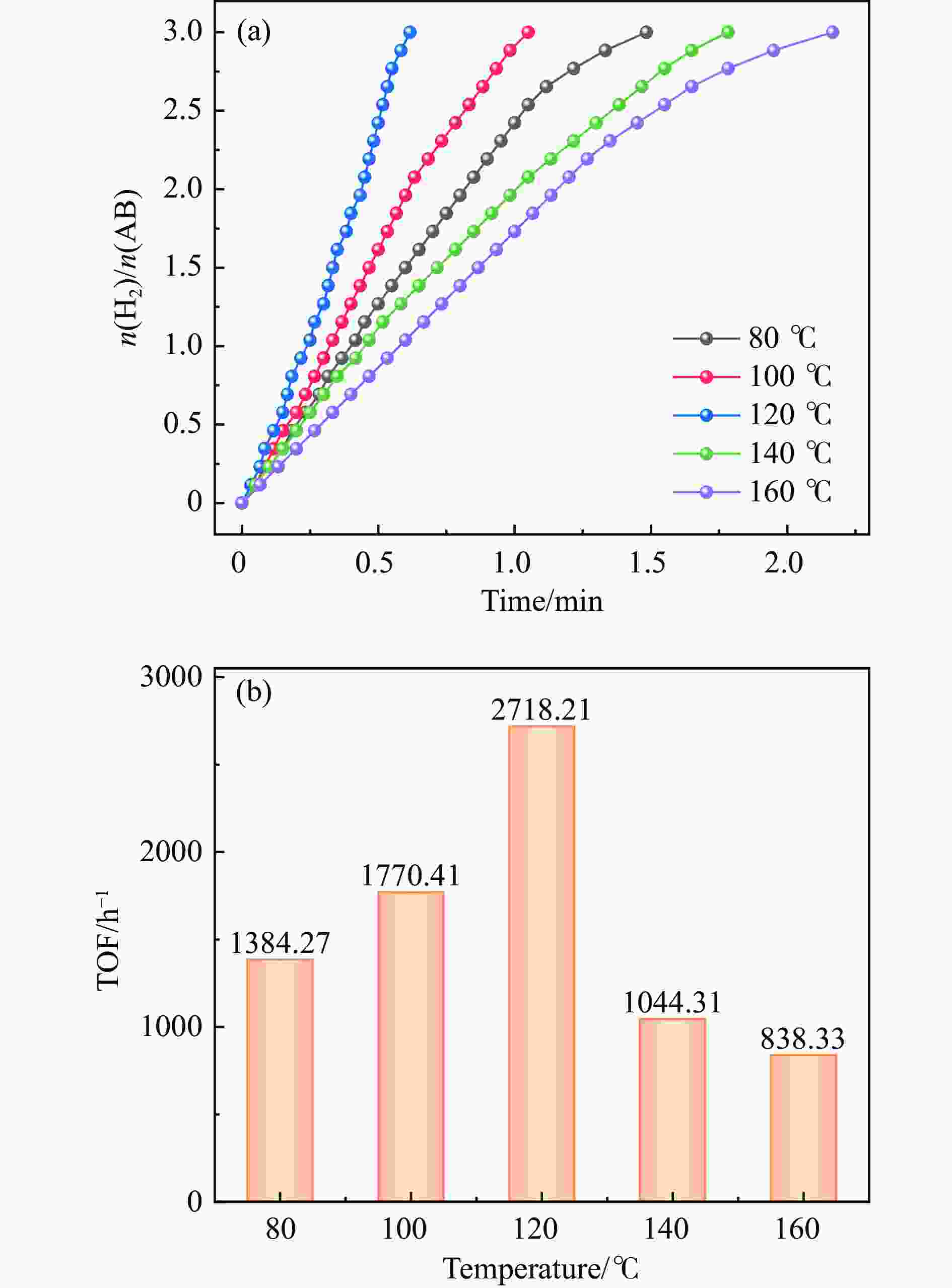
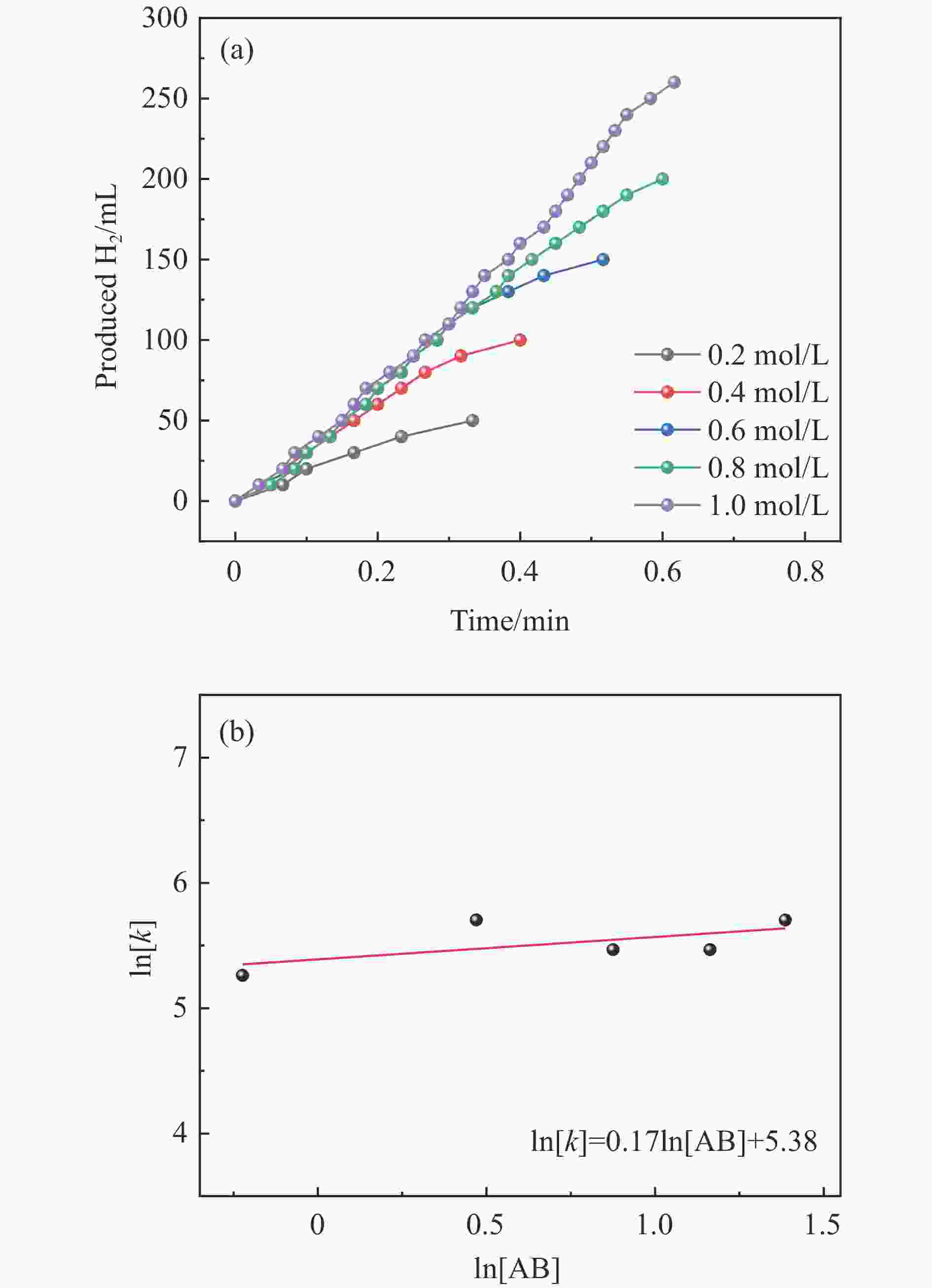
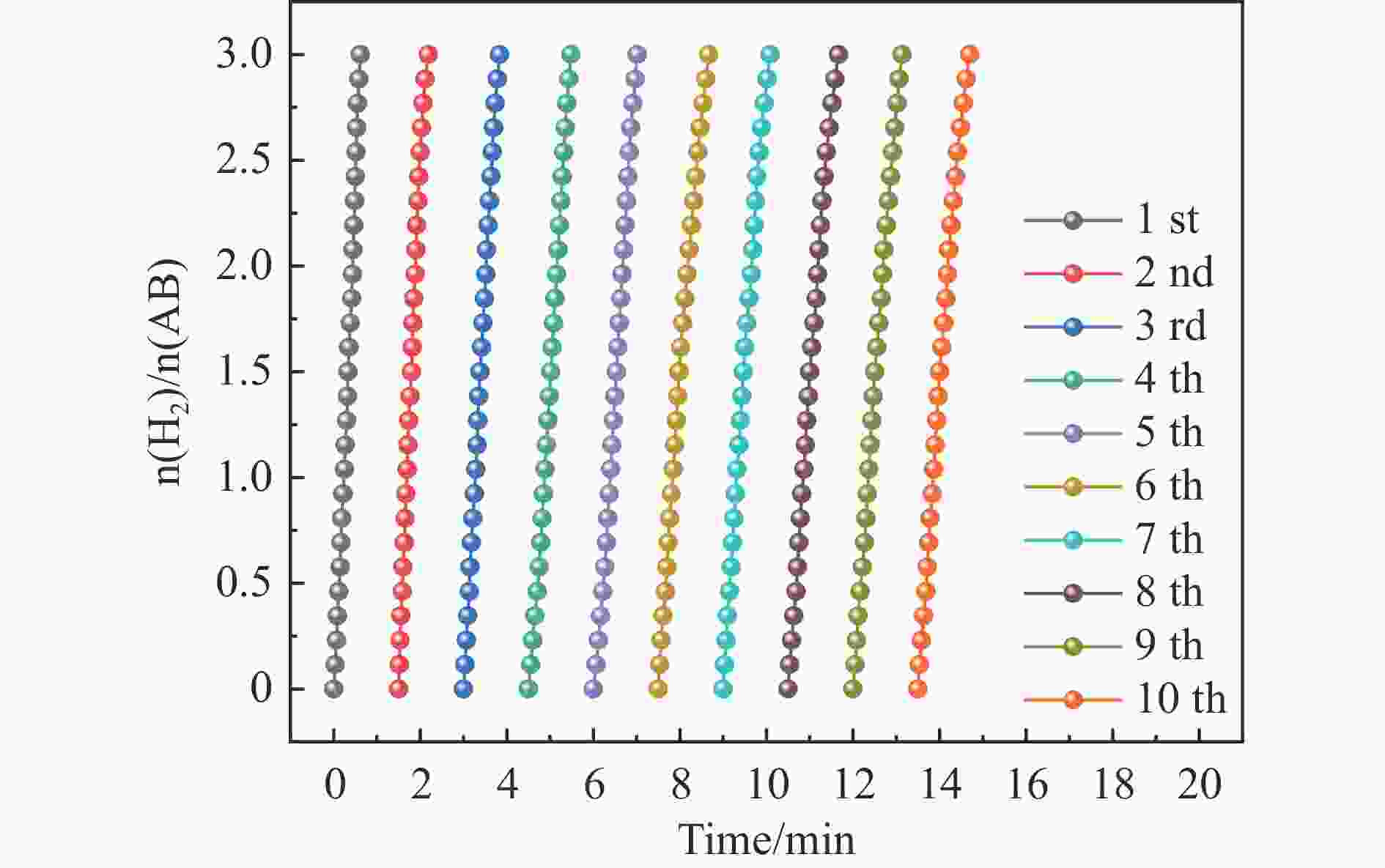
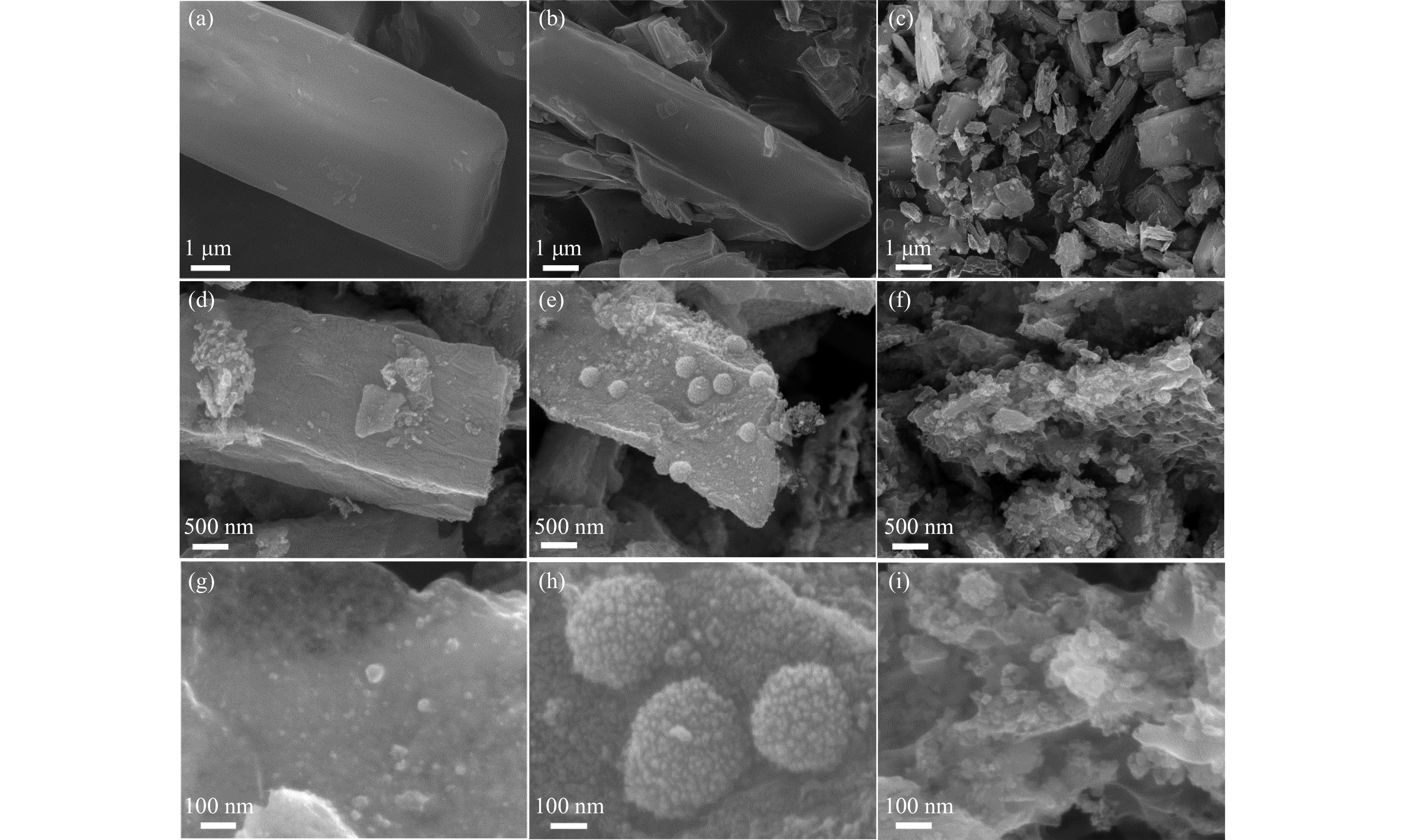
摘要: 以硝酸钴和硝酸铜制备溶液A,苯二甲酸(PTA)和N,N-二甲基甲酰胺(DMF)制备溶液B,两种溶液通过溶剂热法制备Co/Cu拉瓦希尔骨架系列材料(Co/Cu-MIL前驱体),进一步直接碳化前驱体制备出MOFs衍生物,即双金属碳纳米棒(CoxCu1−x/CNR)催化剂。通过SEM、TEM、XRD、XPS等表征手段探究其形貌和组成。结果表明,Co/Cu-MIL经过高温焙烧后成功得到CoxCu1−x/CNR,当x=0.5、溶剂热温度为120 ℃、焙烧温度为650 ℃时得到的催化剂催化活性最优,Co0.5Cu0.5/CNR催化剂催化氨硼烷(AB)水解制氢的TOF值为2718.21 h−1,反应的活化能为51.64 kJ/mol,且催化剂的循环稳定性较好,在循环10次后催化活性虽然有所下降,但对AB仍然保持100%的转化率。
-
关键词:
- 拉瓦希尔骨架系列材料 /
- MOFs衍生物 /
- 双金属碳纳米棒催化剂 /
- 氨硼烷 /
- 水解制氢
Abstract: Solution A was prepared with cobalt nitrate and copper nitrate, and solution B was prepared with phenyldicarboxylic acid(PTA) and N,N-dimethylformamide(DMF), and the two solutions were used to prepare Co/Cu Lavashield skeleton series materials(Co/Cu-MIL precursors) by solvothermal method, and the further direct carbonization of the precursor system prepared the MOFs derivatives, i.e., bimetallic carbon nanorods(CoxCu1−x/CNR) catalyst. The morphology and composition were explored by SEM, TEM, XRD, XPS and other characterization means. The results showed that CoxCu1−x/CNR was successfully obtained after Co/Cu-MIL was roasted at high temperature, and the catalytic activity of the catalyst obtained was optimal when x=0.5, the solvent heat temperature was 120°C, and the roasting temperature was 650 ℃. The TOF value of the Co0.5Cu0.5/CNR catalyst catalyzed the hydrolysis of ammonia borane (AB) for the production of hydrogen was 2718.21 h−1, and the reaction The activation energy was 51.64 kJ/mol, and the catalyst had good cycling stability, and the catalytic activity decreased after 10 cycles, but still maintained 100% conversion of AB. -
表 1 钴铜催化剂催化氨硼烷水解制氢的催化活性
Table 1 The reported catalytic activity of cobalt-copper bimetallic catalysts for the hydrolysis of ammonia borane to produce hydrogen
Catalyst Temp./
℃TOF/
h−1Ea/
(kJ·mol−1)Ref. Co0.5Cu0.5/CNR 25 2718.21 51.64 this work Cu0.4Co0.6/BN nanofibers 25 505.2 21.8 [39] CuCo(O)@CN 25 744 33.8 [40] Cu@Co/rGO 25 522 51.3 [41] CuCo2O4 25 2640 23.6 [42] Cu2O-CoO 25 2046 34.1 [43] Cu0.3@Cu0.7CoOx@GO 25 2676 35.4 [44] Co40Cu60@ S16LC-20 25 984 38.1 [45] CuO-Co3O4 25 2004 39.6 [46] -
[1] MBOYI C D, POINSOT D, ROGER J, et al. The hydrogen-storage challenge: Nanoparticles for metal-catalyzed ammonia borane dehydrogenation[J]. Small,2021,17(44):2102759. doi: 10.1002/smll.202102759 [2] YANG Z X, LI X G, YAO Q L, et al. 2022 roadmap on hydrogen energy from production to utilizations[J]. Rare Metals,2022,41:3251−3267. doi: 10.1007/s12598-022-02029-7 [3] 吴慧, 郑君宁, 左佑华, 等. NiPd/TiO2催化剂的制备及催化甲酸分解制氢[J]. 精细化工, 2023.WU Hui, ZHENG Junning, ZUO Youhua, et al. Preparation of NiPd/TiO2 catalysts and catalytic hydrogen production from formic acid decomposition[J]. Fine Chem, 2023.) [4] WAN C, ZHOU L, XU S M, et al. Defect engineered mesoporous graphitic carbon nitride modified with AgPd nanoparticles for enhanced photocatalytic hydrogen evolution from formic acid[J]. Chem Eng J,2022,429:132388. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2021.132388 [5] MORAD Z, KARIM T, ANTONIO J N, et al. Effective photocatalytic conversion of formic acid using iron, copper and sulphate doped TiO2[J]. J. Cent. South Univ.,2022,29(11):3592−3607. doi: 10.1007/s11771-022-5172-9 [6] 梁雨, 李贵, 郑君宁, 等. NiPt/SBA-15 纳米催化剂的制备及其催化水合肼分解产氢性能研究[J]. 燃料化学学报,2023,51(5):684−692.LIANG Yu, LI Gui, ZHENG Junning, et al. Preparation of NiPt/SBA-15 nanocatalyst and its catalytic performance for the dehydrogenation of hydrous hydrazine[J]. J Fuel Chem Technol,2023,51(5):684−692. [7] 曹云钟, 郑君宁, 吴慧, 等. Pt基催化剂催化氨硼烷水解产氢的研究进展[J]. 稀有金属,2023,47(8):1122−1131.CAO Yunzhong, ZHENG Junning, WU Hui, et al. Advances in hydrogen production by ammonia borane hydrolysis over Pt-based catalysts[J]. Rare Met,2023,47(8):1122−1131. [8] KINSIZ B N, FILIZ B C, DEPREN S K, et al. Nano-casting procedure for catalytic cobalt oxide bead preparation from calcium-alginate capsules: Activity in ammonia borane hydrolysis reaction[J]. Applied Materials Today,2021,22:100952. doi: 10.1016/j.apmt.2021.100952 [9] CAI C, HAN S B, LIU W, et al. Tuning catalytic performance by controlling reconstruction process in operando condition[J]. Appl. Catal. , B,2020,260:118103. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2019.118103 [10] LI Y, HU M W, WANG J S, et al. DFT studies on the Ru-catalyzed hydrolysis of ammonia borane[J]. J. Organomet. Chem.,2019,899:120913. doi: 10.1016/j.jorganchem.2019.120913 [11] 李燕, 邓雨真, 俞晶铃, 等. 氨硼烷分解制氢及其再生的研究进展[J]. 化工进展,2019,38(12):5330−5338.LI Yan, DENG Yuzhen, YU Jingling, et al. Research progress in hydrogen production from decomposition of ammonia borane and its regeneration[J]. Chem. Ind. Eng. Prog.,2019,38(12):5330−5338. [12] DEMIRCI U B. Mechanistic insights into the thermal decomposition of ammonia borane, a material studied for chemical hydrogen storage[J]. Inorg. Chem. Front.,2021,8:1900−1930. doi: 10.1039/D0QI01366H [13] SEMIZ L. Hydrogen generation from ammonia borane by polymer supported platinum films[J]. Chem. Phys. Lett.,2021,767:138365. doi: 10.1016/j.cplett.2021.138365 [14] 王小燕, 张若凡, 司航, 等. 椰壳炭负载钌催化剂的制备及其催化氨硼烷水解制氢性能[J]. 石油炼制与化工,2023,54(7):64−70.WANG Xiaoyan, ZHANG Ruofan, SI Hang, et al. Preparation of coconut shell charcoal-loaded ruthenium catalysts and their catalytic performance for hydrogen production from hydrolysis of ammonia borane[J]. Pet Process Petrochem,2023,54(7):64−70. [15] 任杨斌, 范燕平, 刘宪云, 等. 镍基催化剂催化氨硼烷水解产氢研究进展[J]. 中国材料进展,2022,41(4):288−295.REN Yangbin, FAN Yanping, LIU Xianyun, et al. Research progress on hydrogen generation by catalytic hydrolysis of ammonia borane over Ni catalysts[J]. Materials China,2022,41(4):288−295. [16] AKBAYRAK S, OZKAR S. Ammonia borane as hydrogen storage materials[J]. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy,2018,43(40):18592−18606. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2018.02.190 [17] 邱小魁, 张若凡, 王小燕, 等. 竹茹丝炭负载钌催化剂光催化氨硼烷水解产氢研究[J]. 无机盐工业,2023,55(10):153−158.QIU Xiaokui, ZHANG Ruofan, WANG Xiaoyan, et al. Hydrogen production by photocatalytic hydrolysis of ammonia borane over Bamboo Rhizoma Pinelliae silk charcoal loaded ruthenium catalysts[J]. Inorg Chem Ind,2023,55(10):153−158. [18] LU Q, HUTCHINGS G S, YU W, et al. Highly porous non-precious bimetallic electrocatalysts for efficient hydrogen evolution[J]. Nat. Commun.,2015,6(1):6567. doi: 10.1038/ncomms7567 [19] SUKACKIENĖ Z, VALECKYTĖ G, KEPENIENĖ V, et al. Non-precious metals catalysts for hydrogen generation[J]. Coat.,2023,13(10):1740. doi: 10.3390/coatings13101740 [20] GUPTA S, FERNANDES R, PATEL R, et al. A review of cobalt-based catalysts for sustainable energy and environmental applications[J]. Appl. Catal. , A,2023,661:119254. doi: 10.1016/j.apcata.2023.119254 [21] 黄康, 朱梅婷, 张飞鹏, 等. 一种高效双功能电催化剂 CoP/Co@ NPC@ rGO的制备[J]. 工程科学学报,2020,42(1):91−98.(HUANG Kang, ZHU Meiting, ZHANG Feipeng, et al. Preparation of CoP/Co@NPC@rGO nanocomposites with an efficient bifunctional electrocatalyst for hydrogen evolution and oxygen evolution reaction[J]. Chin J Eng,2020,42(1):91−98. [22] YAN J M, ZHANG X B, SHIOYAMA H, et al. Room temperature hydrolytic dehydrogenation of ammonia borane catalyzed by Co nanoparticles[J]. J. Power Sources,2010,195(4):1091−1094. doi: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2009.08.067 [23] SANG W L, WANG C Y, ZHANG X H, et al. Dendritic Co0.52Cu0.48 and Ni0.19Cu0.81 alloys as hydrogen generation catalysts via hydrolysis of ammonia borane[J]. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy,2017,42(52):30691−30703. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2017.10.130 [24] LU D S, LIAO J Y, ZHONG S D, et al. Cu0.6Ni0.4Co2O4 nanowires, a novel noble-metal-free catalyst with ultrahigh catalytic activity towards the hydrolysis of ammonia borane for hydrogen production[J]. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy,2018,43(11):5541−5550. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2018.01.129 [25] LI H, EDDAOUDI M, O’KEEFFE M. Design and synthesis of an exceptionally stable and highly porous metalorganic framework[J]. Nature,1999,402:276−279. doi: 10.1038/46248 [26] DE VILLENOISY T, ZHENG X, WONG V, et al. Principles of design and synthesis of metal derivatives from MOFs[J]. Adv. Mater. , 2023: 2210166. [27] PODOR R, LE GOFF X, LAUTRU J, et al. Direct observation of the surface topography at high temperature with SEM[J]. Microsc. Microanal.,2020,26(3):397−402. doi: 10.1017/S1431927620001348 [28] 陈峰, 黄莹莹, 颜桂炀, 等. 氧化铜/氧化锌/3A分子筛光催化剂的制备及其可见光脱氮性能[J]. 应用化学,2015,32(9):1040−1047CHEN Feng, HUANG Yingying, YAN Guiyang, et al. Preparation and visible light denitrification performance of copper oxide/Zinc oxide/3A molecular sieve photocatalyst[J]. Chin. J. Appl. Chem,2015,32(9):1040−1047. [29] CHOI W S, SHIN H C. Microporous sponge structure with copper-cobalt oxide hybrid nanobranches[J]. J. Alloys Compd.,2017,692:670−675. doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2016.09.090 [30] DING S, ZHU C, HOJO H, et al. Insights into the effect of cobalt substitution into copper-manganese oxides on enhanced benzene oxidation activity[J]. Appl. Catal. , B,2023,323:122099. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2022.122099 [31] YANG G. , GUAN S. Y. , SEHRISH M. , et al. Co−CoOx supported onto TiO2 coated with carbon as a catalyst for efficient and stable hydrogen generation from ammonia borane[J]. Green Energy Environ. , 2020. [32] PEI X, SHU H, FENG Y. Preparation of nitrogen-doped carbon-based bimetallic copper-cobalt catalysis based on deep learning and its monitoring application in furfural hydrogenation[J]. Scientific Programming, 2022.https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/7702776 [33] LE S. D. , NISHIMURA S. Effect of support on the formation of CuPd alloy nanoparticles for the hydrogenation of succinic acid[J]. Appl. Catal. B Environ. , 2021, 282: 119619. [34] MOSTAFA M M M, BAJAFAR W, GU L, et al. Electrochemical characteristics of nanosized Cu, Ni, and Zn cobaltite spinel materials[J]. Catal.,2022,12(8):893. [35] ZHANG Q, ZUO J, WANG L, et al. Non noble-metal copper–cobalt bimetallic catalyst for efficient catalysis of the hydrogenolysis of 5-hydroxymethylfurfural to 2, 5-dimethylfuran under mild conditions[J]. ACS omega,2021,6(16):10910−10920. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.1c00676 [36] WAN C, LIANG Y, ZHOU L, et al. Integration of morphology and electronic structure modulation on cobalt phosphide nanosheets to boost photocatalytic hydrogen evolution from ammonia borane hydrolysis[J]. Green Energy Environ. , 2022. [37] CHUAICHAM C, LI W, WILSON K, et al. Surfactant and template-free hydrothermal assembly of Cu2O visible light photocatalysts for trimethoprim degradation[J]. Appl. Catal. B Environ. , 2021, 284: 119741. [38] FENG Y F, WANG H Z, CHEN X D, et al. Simple synthesis of Cu2O-CoO nanoplates with enhanced catalytic activity for hydrogen production from ammonia borane hydrolysis[J]. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy.,2020,45:17164−17173. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2020.04.257 [39] YANG X, LI Q L, LI L L, et al. CuCo binary metal nanoparticles supported on boron nitride nanofibers as highly efficient catalysts for hydrogen generation from hydrolysis of ammonia borane[J]. J. Power Sources,2019,431:135−143. doi: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2019.05.038 [40] YUAN Y, CHEN X, ZHANG X, et al. A MOF-derived CuCo(O)@carbon–nitrogen framework as an efficient synergistic catalyst for the hydrolysis of ammonia borane[J]. Inorg. Chem. Front.,2020,7(10):2043−2049. doi: 10.1039/D0QI00023J [41] DU Y, CAO N, YANG L, et al. One-step synthesis of magnetically recyclable rGO supported Cu@Co core–shell nanoparticles: highly efficient catalysts for hydrolytic dehydrogenation of ammonia borane and methylamine borane[J]. New J. Chem.,2013,37(10):3035−3042. doi: 10.1039/c3nj00552f [42] LIU Q, ZHANG S, LIAO J, et al. CuCo2O4 nanoplate film as a low-cost, highly active and durable catalyst towards the hydrolytic dehydrogenation of ammonia borane for hydrogen production[J]. J. Power Sources,2017,355:191−198. doi: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2017.04.057 [43] FENG Y, WANG H, CHEN X, et al. Simple synthesis of Cu2O–CoO nanoplates with enhanced catalytic activity for hydrogen production from ammonia borane hydrolysis[J]. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy,2020,45(35):17164−17173. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2020.04.257 [44] LI J, REN X, LV H, et al. Highly efficient hydrogen production from hydrolysis of ammonia borane over nanostructured Cu@CuCoOx supported on graphene oxide[J]. J. Hazard. Mater.,2020,391:122199. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.122199 [45] DEKA J R, SAIKIA D, LU N F, et al. Space confined synthesis of highly dispersed bimetallic CoCu nanoparticles as effective catalysts for ammonia borane dehydrogenation and 4-nitrophenol reduction[J]. Appl. Surf. Sci,2021,538:148091. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2020.148091 [46] LIAO J, FENG Y, ZHANG X, et al. CuO-Co3O4 composite nanoplatelets for hydrolyzing ammonia borane[J]. ACS Appl. Nano Mater.,2021,4(8):7640−7649. doi: 10.1021/acsanm.1c00713 -





 下载:
下载: