Effect of metal support interaction in Cu/ZnO catalyst on the hydrogenation of furfural to furfuryl alcohol
-
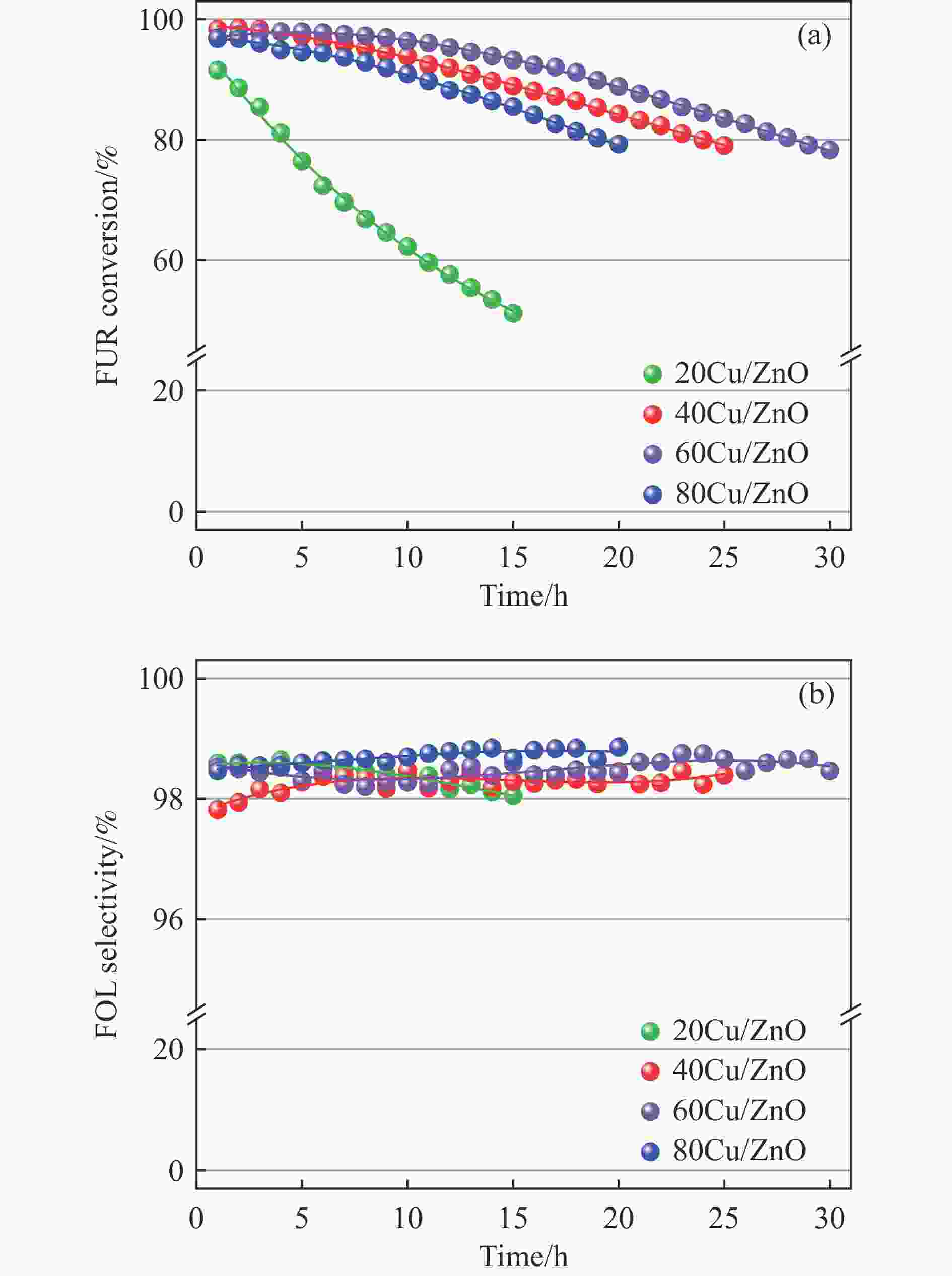
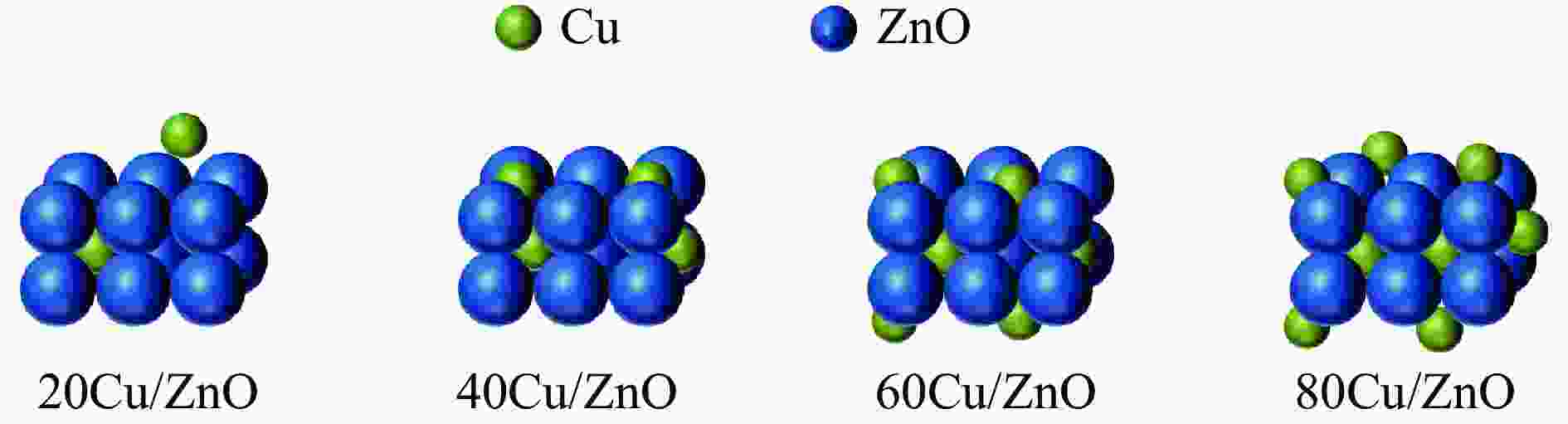
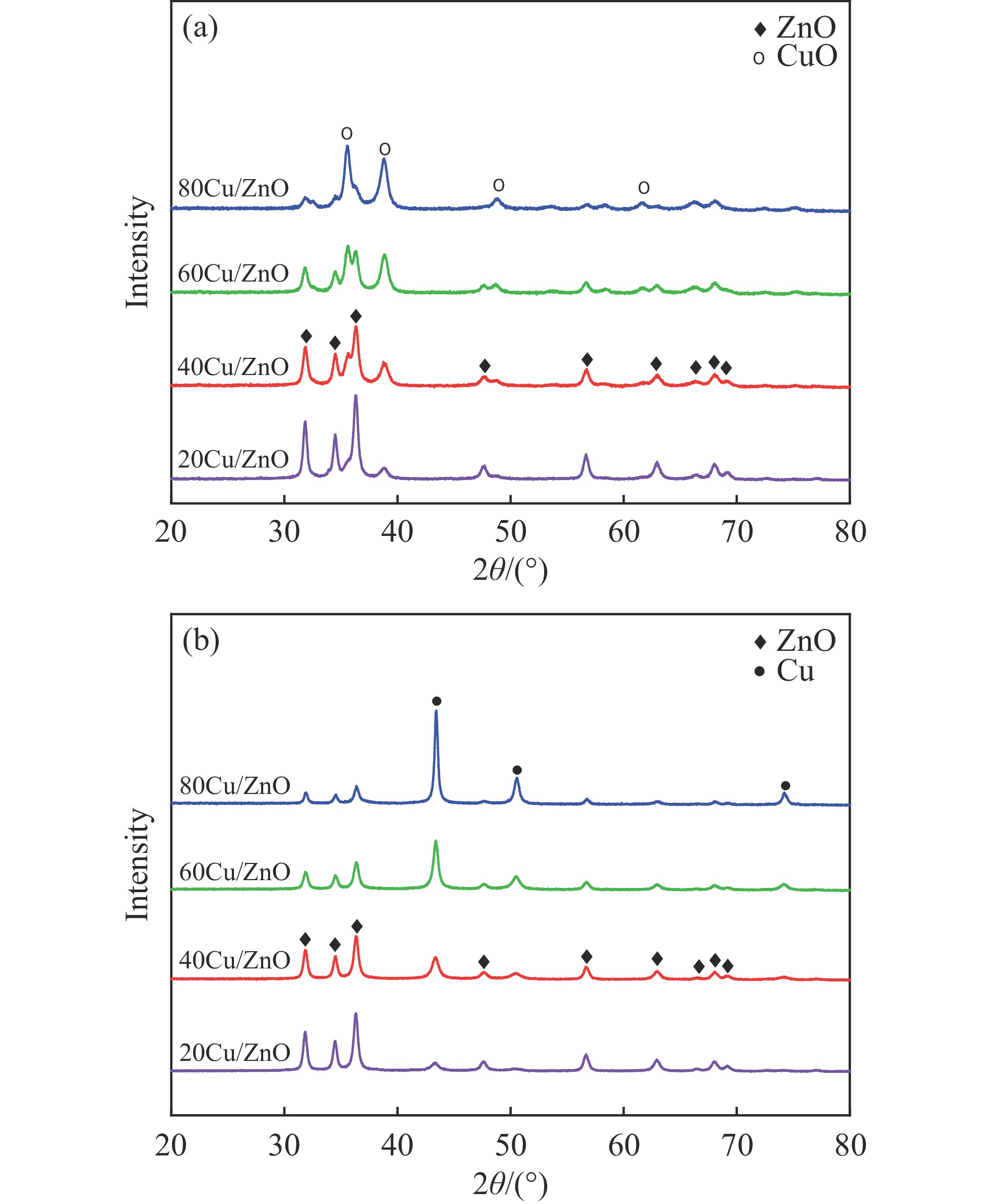
摘要: 本研究考察了共沉淀法制备的Cu/ZnO催化剂中Cu/Zn比例对金属载体强相互作用以及其催化糠醛气相加氢制糠醇反应性能的影响。XRD、H2-TPR、SEM、HRTEM、XPS表征结果表明,Cu/ZnO催化剂体系中存在金属载体强相互作用(SMSI),改变了催化剂的微观结构。ZnO载体对活性金属Cu颗粒形成了不同程度的几何修饰,影响了Cu表面电子状态。Cu/Zn比例影响催化剂SMSI作用,SMSI作用顺序是20Cu/ZnO> 40Cu/ZnO> 60Cu/ZnO> 80Cu/ZnO。在同一反应条件下,20Cu/ZnO催化剂的糠醛转化率高于80%的时间仅为5 h,而60Cu/ZnO催化剂的糠醛转化率高于80%的时间可以达到28 h,表明过强的SMSI作用会抑制催化剂的活性,适当的SMSI作用使Cu/ZnO催化剂在糠醛加氢反应中的稳定性得到提升。Abstract: Cu/ZnO catalysts were prepared by coprecipitation method and the effect of Cu/Zn ratio on the strong metal support interaction was investigated. The effect of SMSI on the performance of furfural hydrogenation to furfuryl alcohol was also studied. The Cu/ZnO catalysts were characterized by H2-TPR, XRD, SEM, TEM and XPS. The results showed that there is strong metal-support interaction (SMSI) in the Cu/ZnO catalyst, which changes the microstructure of the catalyst. ZnO support played the role of geometric modification on the active metal Cu particles, and it changed electronic state of the Cu on the surface. SMSI was affected by the change of Cu/Zn ratio, the order of SMSI action is 20Cu/ZnO> 40Cu/ZnO> 60Cu/ZnO> 80Cu/ZnO. Under the same reaction conditions, the furfural conversion rate of the 20Cu/ZnO was higher than 80% catalyst for only 5 h, while the time of the 60Cu/ZnO catalyst reached 28 h. The results show that the activity of the Cu/ZnO catalyst in the furfural hydrogenation reaction was inhibited by the over-strong SMSI action, and the stability of catalysts in the reaction was improved by appropriate SMSI effect.
-
表 1 新鲜Cu/ZnO催化剂的物理化学性质
Table 1 Physicochemical properties of fresh Cu/ZnO catalysts
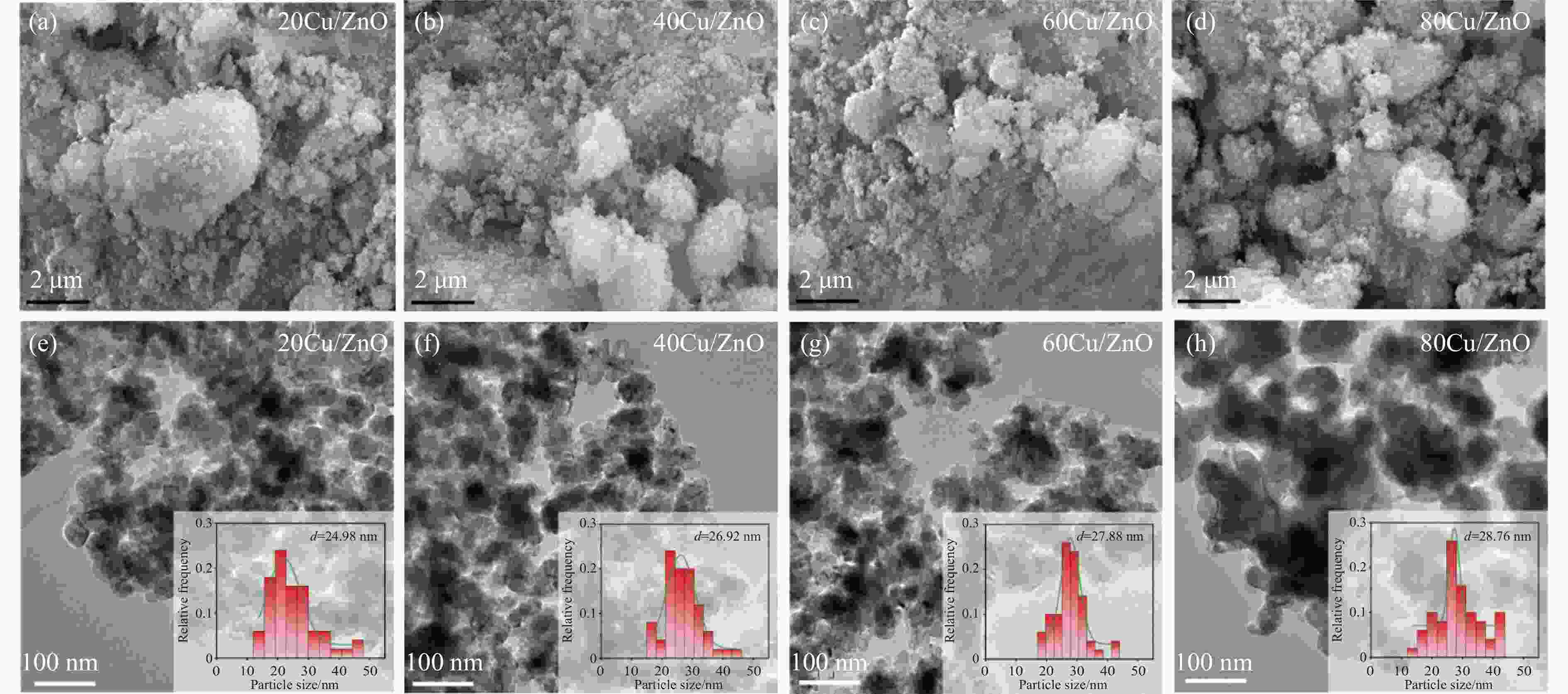
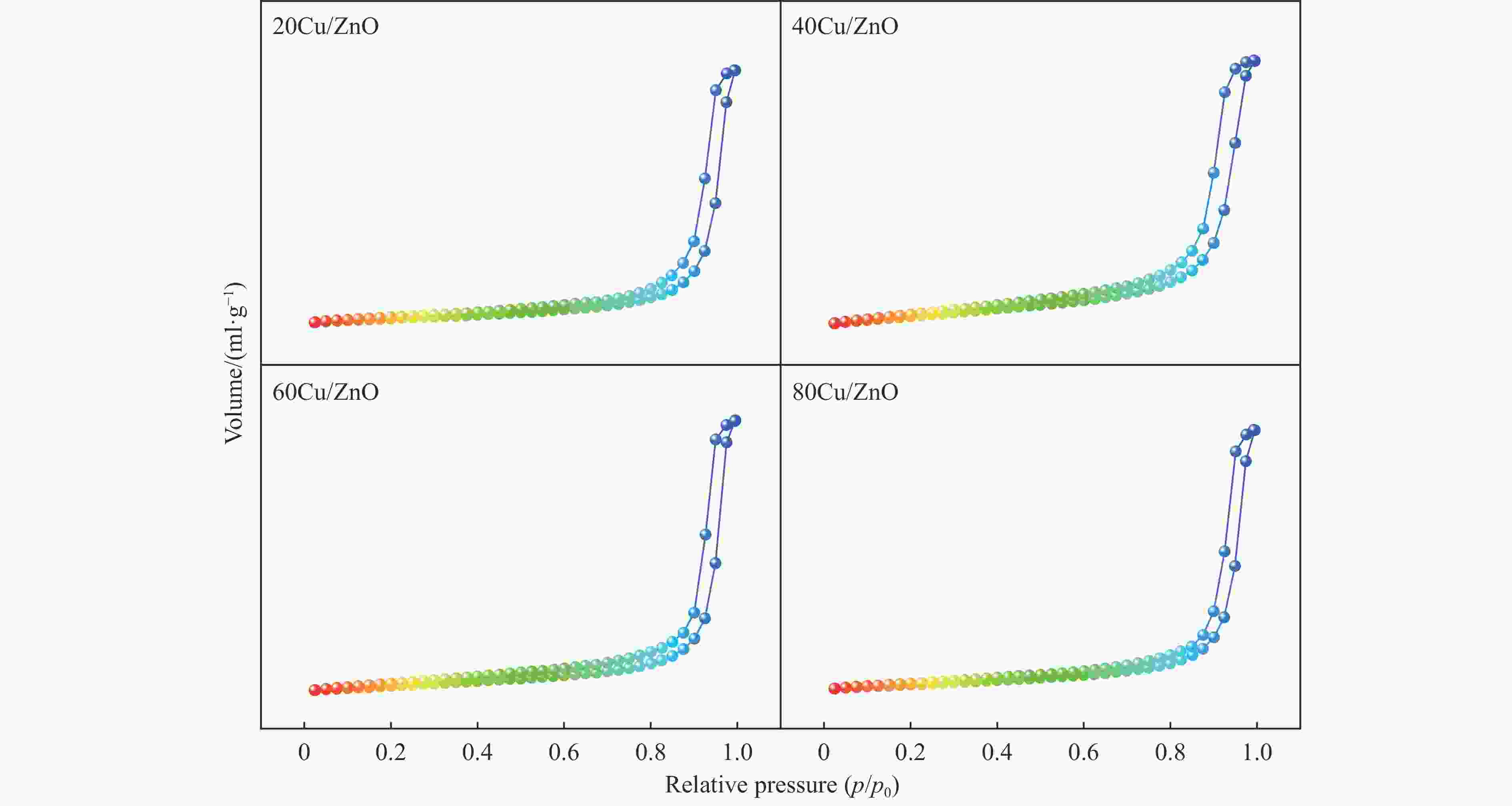
Catalyst sBETa/(m2·g−1) vtotala/(cm3·g−1) dporea/nm dCub/nm dparticlesc/nm dCud/nm DCud/% SCud/(m2·g−1) 20Cu/ZnO 22.9 0.14 24.1 9.3 25.0 8.3 12.1 13.1 40Cu/ZnO 42.5 0.17 18.8 10.6 26.0 13.6 7.4 15.9 60Cu/ZnO 28.5 0.17 24.2 14.4 28.0 21.0 4.8 15.4 80Cu/ZnO 24.2 0.18 24.3 20.2 29.0 16.3 6.1 26.5 a: Determined by nitrogen adsorption; b: Average Cu particle size was calculated using the Scherrer equation; c: Determined by TEM; d: Copper particle size, copper dispersion and exposed metallic copper surface area were determined using N2O-titration. 表 2 催化剂还原峰及酸量
Table 2 Reduction and acidity distribution of different catalysts
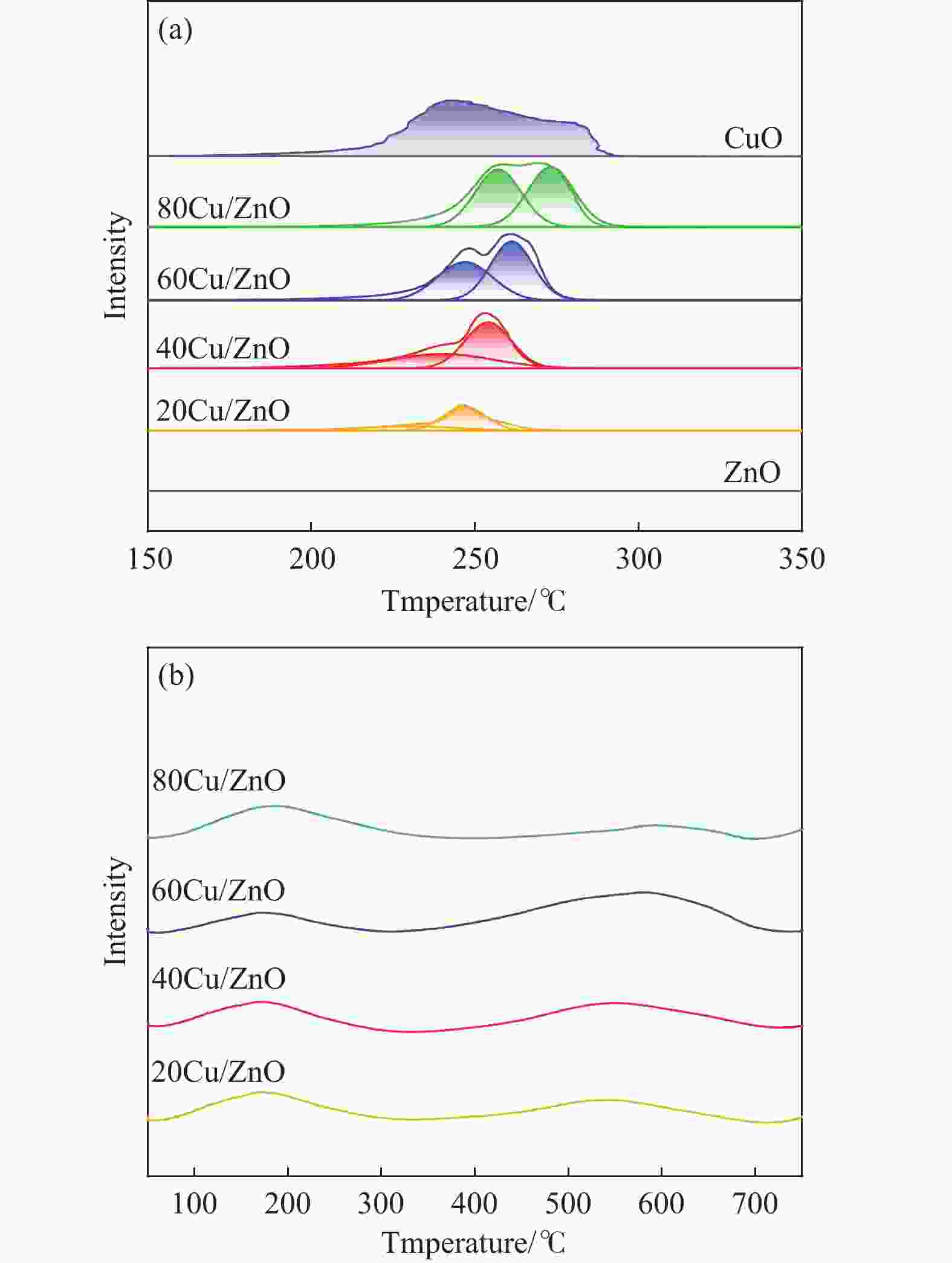
Catalyst α峰 β峰 Relative area Acidity/
(mmol·g−1)Acid site density/
(mmol·m−2)t/℃ fraction/% t/℃ fraction/% 20Cu/ZnO 229.7 28.0 246.9 72.0 2765.8 0.059 0.0025 40Cu/ZnO 240.1 40.6 254.1 59.4 6349.5 0.197 0.0046 60Cu/ZnO 247.0 46.4 261.3 53.6 9424.3 0.113 0.0039 80Cu/ZnO 257.1 49.0 273.2 51.0 10944.3 0.072 0.0029 表 3 还原态Cu/ZnO催化剂表面金属物种在XPS中的分布
Table 3 Distribution of metal species on the surface of reduced Cu/ZnO catalysts in XPS
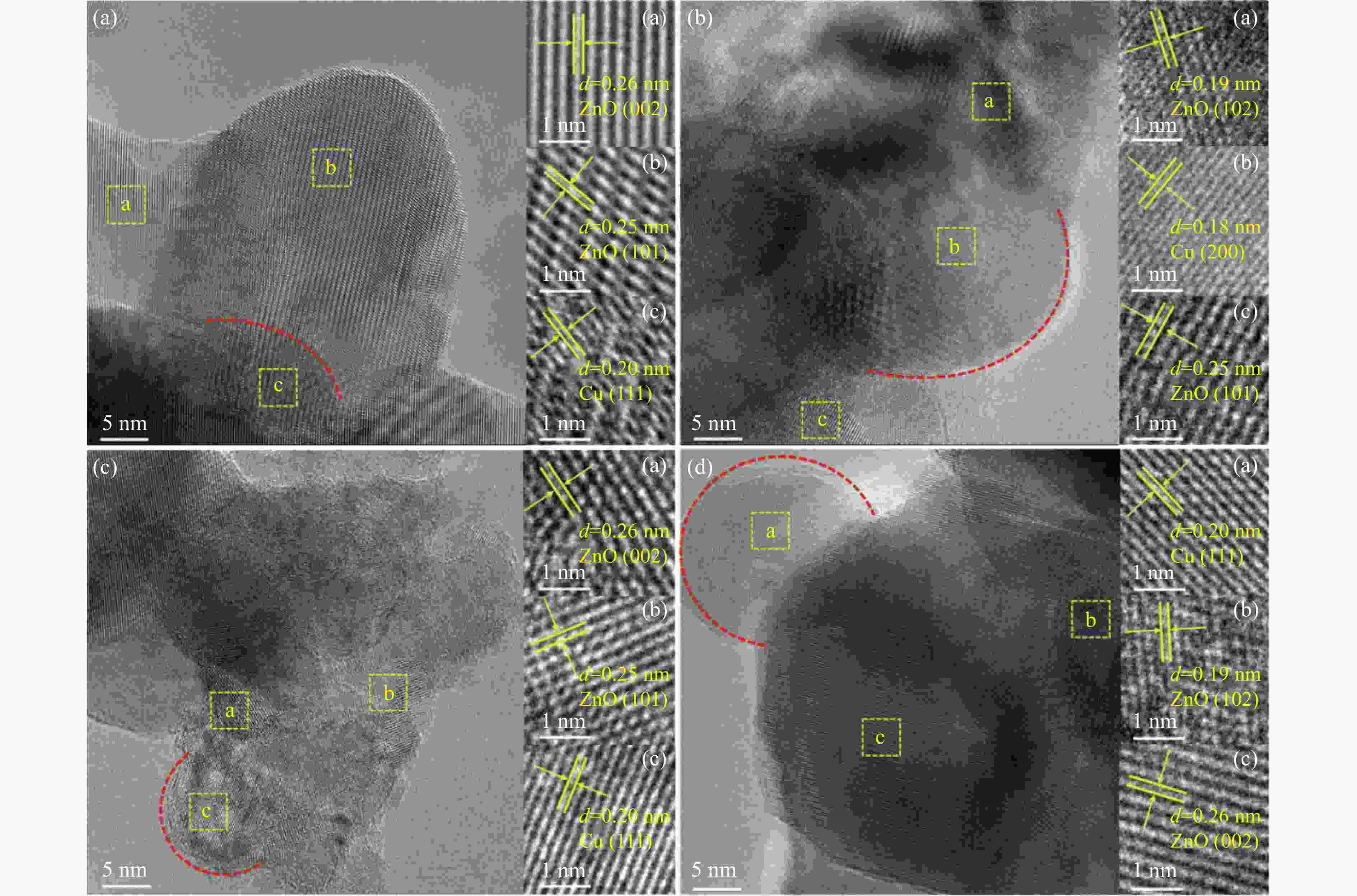
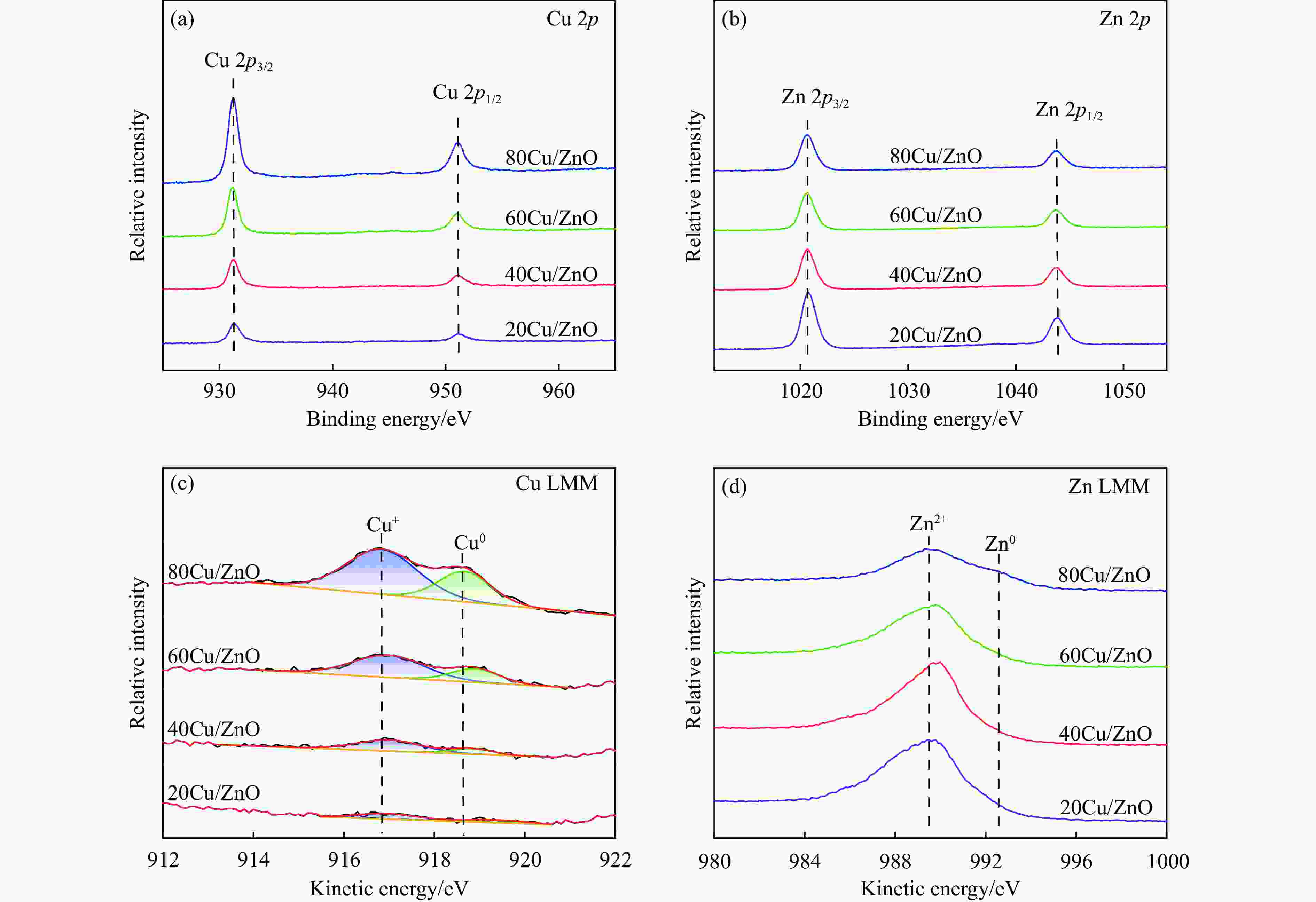
Catalysts BE/eV KE/eV KE/eV x(Cu0)a/% Cu 2p3/2 Zn 2p3/2 Cu+ Cu0 Zn2+ Zn0 Cu0/ (Cu++ Cu0) 20Cu/ZnO 932.4 1020.8 916.96 919.40 989.7 − 33.58 % 40Cu/ZnO 932.3 1020.6 917.00 918.85 990.1 − 23.55 % 60Cu/ZnO 932.4 1020.5 916.98 918.90 990.3 − 29.16 % 80Cu/ZnO 932.5 1020.6 916.83 918.67 988.9 992.4 32.83 % a: Ratio of Cu0 to (Cu++Cu0) obtained by deconvolution of Cu LMM spectra. 表 4 使用后Cu/ZnO催化剂的物理化学性质
Table 4 Physicochemical properties of used Cu/ZnO catalysts
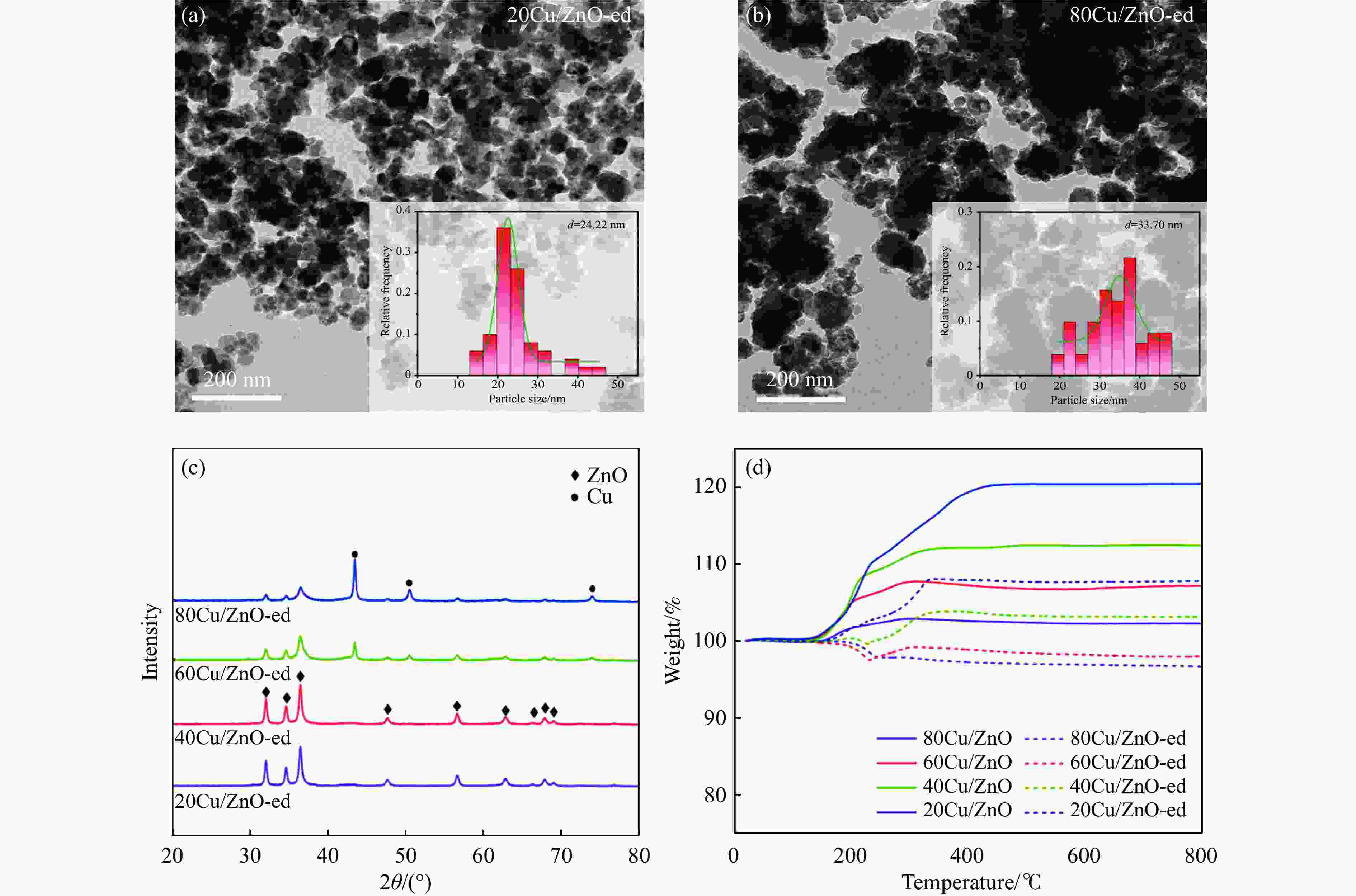
Catalyst dCua/nm dparticles b/nm △Wc/% 20Cu/ZnO-ed 5.2 24.22 5.6 40Cu/ZnO-ed 6.0 − 9.2 60Cu/ZnO-ed 14.4 − 9.2 80Cu/ZnO-ed 20.5 33.70 12.66 a: Average Cu particle size was calculated using the Scherrer equation; b: Determined by TEM; c: Determined by TG. -
[1] LIU H W, HU Q, FAN G L, et al. Surface synergistic effect in well-dispersed Cu/MgO catalysts for highly efficient vapor-phase hydrogenation of carbonyl compounds[J]. Catal Sci Technol,2015,5(8):3960−3969. doi: 10.1039/C5CY00437C [2] DONG F, ZHU Y L, ZHENG H Y, et al. Cr-free Cu-catalysts for the selective hydrogenation of biomass-derived furfural to 2-methylfuran: The synergistic effect of metal and acid sites[J]. J Mol Catal A:Chem,2015,398:140−148. doi: 10.1016/j.molcata.2014.12.001 [3] AN J W, WANG X H, ZHAO J X, et al. Density-functional theory study on hydrogenation of dimethyl oxalate to methyl glycolate over copper catalyst: Effect of copper valence state[J]. Mol Catal,2020,482:110667. doi: 10.1016/j.mcat.2019.110667 [4] KURNIAWAN E, HAYASHI T, HOSAKA S, et al. Selective Vapor-Phase Hydrogenation of Furfural to Furfuryl Alcohol over Cu/Silica Catalysts[J]. Bull Chem Soc Jpn,2023,96(1):8−15. doi: 10.1246/bcsj.20220285 [5] GHASHGHAEE M, SHIRVANI S, GHAMBARIAN M. Kinetic models for hydroconversion of furfural over the ecofriendly Cu-MgO catalyst: An experimental and theoretical study[J]. App Catal A:Gen,2017,545:134−147. doi: 10.1016/j.apcata.2017.07.040 [6] SADJADI S, FARZANEH V, SHIRVANI S, et al. Preparation of Cu-MgO catalysts with different copper precursors and precipitating agents for the vapor-phase hydrogenation of furfural[J]. Korean J Chem Eng,2017,34(3):692−700. doi: 10.1007/s11814-016-0344-7 [7] R. BERTOLINI G, JIMÉNEZ-GÓMEZ C P, CECILIA J A, et al. Gas-Phase Hydrogenation of Furfural to Furfuryl Alcohol over Cu-ZnO-Al2O3 Catalysts Prepared from Layered Double Hydroxides[J]. Catalysts, 2020, 10(5): 486. [8] ALGORABI S, AKMAZ S, KOÇ S N. The investigation of hydrogenation behavior of furfural over sol–gel prepared Cu/ZrO2 catalysts[J]. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol,2020,96(1):47−55. doi: 10.1007/s10971-020-05352-6 [9] JIMÉNEZ-GÓMEZ C P, CECILIA J A, FRANCO-DURO F I, et al. Promotion effect of Ce or Zn oxides for improving furfuryl alcohol yield in the furfural hydrogenation using inexpensive Cu-based catalysts[J]. Mol Catal,2018,455:121−131. doi: 10.1016/j.mcat.2018.06.001 [10] GARCÍA-SANCHO C, MÉRIDA-ROBLES J M, CECILIA-BUENESTADO J A, et al. The Role of Copper in the Hydrogenation of Furfural and Levulinic Acid[J]. Int J Mol Sci,2023,24(3):2443. doi: 10.3390/ijms24032443 [11] ZHENG J W, ZHOU J F, LIN H Q, et al. CO-Mediated Deactivation Mechanism of SiO2-Supported Copper Catalysts during Dimethyl Oxalate Hydrogenation to Ethylene Glycol[J]. J Phys Chem C,2015,119(24):13758−13766. doi: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.5b03569 [12] LI Y W, ZHANG R M, DU L K, et al. Catalytic mechanism of C–F bond cleavage: insights from QM/MM analysis of fluoroacetate dehalogenase[J]. Catal Sci Technol,2016,6(1):73−80. doi: 10.1039/C5CY00777A [13] CERÓN M R, IZQUIERDO M, ALEGRET N, et al. Reactivity differences of Sc3N@C2n(2n = 68 and 80). Synthesis of the first methanofullerene derivatives of Sc3N@D5h -C80[J]. Chem Commun,2016,52(1):64−67. doi: 10.1039/C5CC07416A [14] TAUSTER S J, FUNG S C, BAKER R T K, et al. Strong Interactions in Supported-Metal Catalysts[J]. Science,1981,211(4487):1121−1125. doi: 10.1126/science.211.4487.1121 [15] TAUSTER J S, FUNG C S, GARTEN L R. Strong metal-support interactions. Group 8 noble metals supported on titanium dioxide[J]. J Am Chem Soc,2002,100(1):170−175. [16] TAUSTER J. Strong Metal-Support Interactions[J]. Accounts Chem Res,1987,20(11):121−140. [17] WANG W X, LI X K, ZHANG Y, et al. Strong metal–support interactions between Ni and ZnO particles and their effect on the methanation performance of Ni/ZnO[J]. Catal Sci Technol,2017,7(19):4413−4421. doi: 10.1039/C7CY01119A [18] LIU X Y, LIU M H, LUO Y C, et al. Strong Metal–Support Interactions between Gold Nanoparticles and ZnO Nanorods in CO Oxidation[J]. J Am Chem Soc,2012,134(24):10251−10258. doi: 10.1021/ja3033235 [19] HANSEN P L, WAGNER J B, HELVEG S, et al. Atom-Resolved Imaging of Dynamic Shape Changes in Supported Copper Nanocrystals[J]. Science,2002,295(5562):2053−2055. doi: 10.1126/science.1069325 [20] JIMÉNEZ-GÓMEZ C P, CECILIA J A, DURÁN-MARTÍN D, et al. Gas-phase hydrogenation of furfural to furfuryl alcohol over Cu/ZnO catalysts[J]. J Catal,2016,336:107−115. doi: 10.1016/j.jcat.2016.01.012 [21] 萧垚鑫, 张军, 胡升, 等. 甲醇供氢体系铜锌双金属催化糠醛加氢转化[J]. 化工进展,2023,42(3):1341−1352.XIAO Yaoxin, ZHANG Jun, HU Sheng, et al. Catalytic hydrogenation of furfural by copper and zinc bimetal in methanol hydrogen supply system[J]. Chem Ind Eng Prog,2023,42(3):1341−1352. [22] LI K, CHEN J G. CO2 Hydrogenation to Methanol over ZrO2-Containing Catalysts: Insights into ZrO2 Induced Synergy[J]. ACS Catal,2019,9(9):7840−7861. doi: 10.1021/acscatal.9b01943 [23] SCHUMANN J, EICHELBAUM M, LUNKENBEIN T, et al. Promoting Strong Metal Support Interaction: Doping ZnO for Enhanced Activity of Cu/ZnO: M (M = Al, Ga, Mg) Catalysts[J]. ACS Catal,2015,5(6):3260−3270. doi: 10.1021/acscatal.5b00188 [24] ZHANG S Y, HU Q, FAN G L, et al. The relationship between the structure and catalytic performance Cu/ZnO/ZrO2 catalysts for hydrogenation of dimethyl 1, 4-cyclohexane dicarboxylate[J]. Catal Commun,2013,39:96−101. doi: 10.1016/j.catcom.2013.05.011 [25] ZHANG S Y, LIU Q Y, FAN G L, et al. Highly-Dispersed Copper-Based Catalysts from Cu–Zn–Al Layered Double Hydroxide Precursor for Gas-Phase Hydrogenation of Dimethyl Oxalate to Ethylene Glycol[J]. Catal Lett,2012,142(9):1121−1127. doi: 10.1007/s10562-012-0871-8 [26] 孔祥鹏, 游新明, 元培红, 等. 助剂对于Cu/ZnO催化剂结构特征及催化草酸二甲酯加氢合成乙二醇反应性能的影响[J]. 燃料化学学报(中英文),2023,51(6):794−803. doi: 10.1016/S1872-5813(22)60073-2KONG Xiangpeng, YOU Xinming, YUAN Peihong, et al. Effects of Additives on structural characteristics and catalytic performance of Cu/ZnO catalyst for hydrogenation of Dimethyl oxalate to ethylene glycol[J]. J Fuel Chem Technol,2023,51(6):794−803. doi: 10.1016/S1872-5813(22)60073-2 [27] 黄玉辉, 任国卿, 孙蛟, 等. Cu/ZnO催化糠醛气相加氢制2-甲基呋喃的研究[J]. 燃料化学学报,2016,44(11):1349−1355.HUANG Yuhui, REN Guoqing, SUN Jiao, et al. Study on gas phase hydrogenation of furfural catalyzed by Cu/ZnO to 2-methylfuran[J]. J Fuel Chem Technol,2016,44(11):1349−1355. [28] 黄玉辉, 任国卿, 孙蛟, 等. 沉淀剂对CuZnAl催化剂糠醛气相加氢制糠醇选择性的影响[J]. 燃料化学学报,2016,44(6):726−731.HUANG Yuhui, REN Guoqing, SUN Jiao, et al. Effect of precipitator on selectivity of furfural gas phase hydrogenation to furfuryl alcohol by CuZnAl catalyst[J]. J Fuel Chem Technol,2016,44(6):726−731. [29] YUAN Z L, WANG L N, WANG J H, et al. Hydrogenolysis of glycerol over homogenously dispersed copper on solid base catalysts[J]. Appl Catal B:Environ,2011,101(3-4):431−440. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2010.10.013 [30] LI H B, CUI Y Y, LIU Y X, et al. Highly efficient Ag-modified copper phyllosilicate nanotube: Preparation by co-ammonia evaporation hydrothermal method and application in the selective hydrogenation of carbonate[J]. J Mater Sci Technol,2020,47(12):29−37. [31] 于冬冬, 于欣瑞, 张雅静, 等. 糠醛气相加氢制备糠醇Cu/SiO2催化剂的失活机理研究[J]. 燃料化学学报(中英文),2023,51(12):1751−1760. doi: 10.1016/S1872-5813(23)60362-7YU Dongdong, YU Xinrui, ZHANG Yajing, et al. Study on deactivation mechanism of Furfuryl alcohol Cu/SiO2 catalyst prepared by furfural Gasification[J]. J Fuel Chem Technol,2023,51(12):1751−1760. doi: 10.1016/S1872-5813(23)60362-7 [32] PARK S W, JOO O S, JUNG K D, et al. Development of ZnO/Al2O3 catalyst for reverse-water-gas-shift reaction of CAMERE (carbon dioxide hydrogenation to form methanol via a reverse-water-gas-shift reaction) process[J]. Appl Catal A:Gen,2001,211(1):81−90. doi: 10.1016/S0926-860X(00)00840-1 [33] MENG H, LIU J G, DU Y L, et al. Novel Cu-based oxides catalyst from one-step carbothermal reduction decomposition method for selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3[J]. Catal Commun,2019,119:101−105. doi: 10.1016/j.catcom.2018.10.023 [34] 丛昱, 包信和, 张涛, 等. CO2加氢合成甲醇的超细Cu-ZnO-ZrO2催化剂的表征[J]. 催化学报,2000,(4):314−318.CONG Yu, BAO Xinhe, ZHANG Tao, et al. Characterization of ultrafine Cu-ZnO-ZrO2 catalyst for hydrogenation of CO2 to methanol[J]. Chin J Catal,2000,(4):314−318. [35] JIMÉNEZ-GÓMEZ C P, CECILIA J A, ALBA-RUBIO A C, et al. Tailoring the selectivity of Cu-based catalysts in the furfural hydrogenation reaction: Influence of the morphology of the silica support[J]. Fuel,2022,319:123827. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2022.123827 [36] TU Y J, CHEN Y W. Effects of Alkaline-Earth Oxide Additives on Silica-Supported Copper Catalysts in Ethanol Dehydrogenation[J]. Ind Eng Chem Res,1998,37(7):2618−2622. doi: 10.1021/ie9708135 [37] BEHRENS M, STUDT F, KASATKIN I, et al. The Active Site of Methanol Synthesis over Cu/ZnO/Al2O3 Industrial Catalysts[J]. Science,2012,336(6083):893−897. doi: 10.1126/science.1219831 [38] NIE R F, LEI H, PAN S Y, et al. Core–shell structured CuO–ZnO@H-ZSM-5 catalysts for CO hydrogenation to dimethyl ether[J]. Fuel, 2012, 96419-425. [39] TURCO M, BAGNASCO G, CAMMARANO C, et al. Cu/ZnO/Al2O3 catalysts for oxidative steam reforming of methanol: The role of Cu and the dispersing oxide matrix[J]. Appl Catal B:Environ,2007,77(1-2):46−57. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2007.07.006 [40] CHEN F, LIANG J M, WANG F, et al. Improved catalytic activity and stability of Cu/ZnO catalyst by boron oxide modification for low-temperature methanol synthesis[J]. Chem Eng J, 2023, 458. [41] KARIM W, SPREAFICO C, KLEIBERT A, et al. Catalyst support effects on hydrogen spillover[J]. Nature,2017,541(7635):68−71. doi: 10.1038/nature20782 [42] ZHANG S, PLESSOW P N, WILLIS J J, et al. Dynamical Observation and Detailed Description of Catalysts under Strong Metal–Support Interaction[J]. Nano Lett,2016,16(7):4528−4534. doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.6b01769 [43] YANG X, CHEN H, MENG Q, et al. Insights into influence of nanoparticle size and metal–support interactions of Cu/ZnO catalysts on activity for furfural hydrogenation[J]. Catal Sci Technol,2017,7(23):5625−5634. doi: 10.1039/C7CY01284E [44] 陈列. 晶化的介孔金属氧化物的合成与电化学储能性能研究[D]. 南京大学, 2015.CHEN Lie. Synthesis and electrochemical energy storage Performance of crystallized mesoporous metal oxides [D]. Nanjing University, 2015.) [45] VAN DEELEN T W, HERNÁNDEZ MEJÍA C, DE JONG K P. Control of metal-support interactions in heterogeneous catalysts to enhance activity and selectivity[J]. Nat Catal,2019,2(11):955−970. doi: 10.1038/s41929-019-0364-x [46] CHEN H, CUI H S, LV Y, et al. CO2 hydrogenation to methanol over Cu/ZnO/ZrO2 catalysts: Effects of ZnO morphology and oxygen vacancy[J]. Fuel,2022,314:123035. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2021.123035 [47] 海雪清, 谭静静, 何静, 等. CuCo双金属催化剂催化糠醛加氢制备1, 5-戊二醇的研究[J]. 燃料化学学报(中英文),2023,51(7):959−969. doi: 10.1016/S1872-5813(23)60334-2HAI Xueqing, TAN Jingjing, HE Jing, et al. Preparation of 1, 5-pentanediol by hydrogenation of furfural with CuCo bimetallic catalyst[J]. J Fuel Chem Technol,2023,51(7):959−969. doi: 10.1016/S1872-5813(23)60334-2 [48] GUO T, GUO Q, LI S Z, et al. Effect of surface basicity over the supported Cu-ZnO catalysts on hydrogenation of CO2 to methanol[J]. J Catal,2022,407:312−321. doi: 10.1016/j.jcat.2022.01.035 [49] ZHANG J Y, JIA Z, YU S T, et al. Regulating the Cu0-Cu+ ratio to enhance metal-support interaction for selective hydrogenation of furfural under mild conditions[J]. Chem Eng J, 2023, 468. [50] JIMÉNEZ-GÓMEZ C P, CECILIA J A, MORENO-TOST R, et al. Selective Production of 2-Methylfuran by Gas-Phase Hydrogenation of Furfural on Copper Incorporated by Complexation in Mesoporous Silica Catalysts[J]. ChemSusChem,2017,10(7):1448−1459. doi: 10.1002/cssc.201700086 [51] LI F, CAO B, MA R, et al. Performance of Cu/TiO2 -SiO2 catalysts in hydrogenation of furfural to furfuryl alcohol[J]. Can J Chem Eng,2016,94(7):1368−1374. doi: 10.1002/cjce.22503 [52] VASILIADOU E, EGGENHUISEN T, MUNNIK P, et al. Synthesis and performance of highly dispersed Cu/SiO2 catalysts for the hydrogenolysis of glycerol[J]. Appl Catal B: Environ, 2014, 145108-119. -




 下载:
下载: